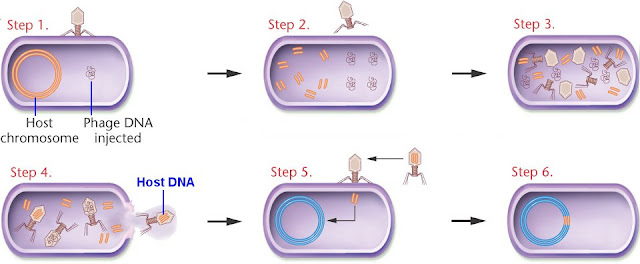
Bacteriophage Life Cycle . The family name comes from the ancient greek word ‘μικρός’ (mikrós), which translate to small, reflecting the size of their genomes. The challenge with natural bacteriophages.
Bacteriophage characteristics and replication of lytic from microbiologynotes.org
There are 2 types of lifecycles that occur in the bacteriophage: It is also called virulent or infectious cycle. Life cycle the life cycle of a lytic phage is illustrated in figure 3.
Bacteriophage characteristics and replication of lytic
Bacteriophage exhibits two major types of life cycles: Lytic cycle or virulent cycle; Lytic cycle (virulent cycle) in this cycle, a bacteriophage enters bacteria and kills them. 1) lytic cycle 2) lysogenic cycle 1) lytic cycle:
Source: www.cronodon.com
Check Details
M13 uses the f pilus of e. It includes the following steps: During infection a phage attaches to a bacterium and inserts its genetic material into the cell. Lytic or virulent phages are phages, which multiply in bacteria and kill the cell by lysis at the end of the life cycle. (lysis of host cell) temperate / avirulent cycle.
Source: premabotany.blogspot.com
Check Details
There are 2 types of lifecycles that occur in the bacteriophage: 1) lytic cycle 2) lysogenic cycle 1) lytic cycle: It includes the lytic phages. The phages of a lytic cycle can infect or kill the host cell, due to which the cycle is known as a virulent phase. In lytic cycle, virus that is the bacteriophage causes lysis of.
Source: www.slideserve.com
Check Details
M13 uses the f pilus of e. Bacteriophages exhibit two types of lifecycles, lytic / virulent cycle: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of phage m13. Bacteriophages attach to targeted bacteria, insert genetic information, replicate using the host bacterium, burst the cell wall, thereby destroying the bacterium, and move on to kill yet more bacteria. Lytic.
Source: mybedsidemanner.blogspot.com
Check Details
Phage life cycles behind bacterial. Life cycle of bacteriophage phages exhibit two different types of life cycle virulent or lytic cycle temperate or lysogenic cycle intracellular multiplication of the phage culminates in lysis of the host bacterium and the release of progeny virions. Life cycle the life cycle of a lytic phage is illustrated in figure 3. Bacteria eating virus.
Source: logyofbio.blogspot.com
Check Details
Phages are present in every environment and shape up every bacterial population in both active and passive ways. Bacteria eating virus is called bacteriophage. During infection a phage attaches to a bacterium and inserts its genetic material into the cell. It then releases a progeny virus. In the lytic cycle, a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release.
Source: cronodon.com
Check Details
It then releases a progeny virus. Life cycle of bacteriophage phages exhibit two different types of life cycle virulent or lytic cycle temperate or lysogenic cycle intracellular multiplication of the phage culminates in lysis of the host bacterium and the release of progeny virions. It includes the following steps: In the virulent or lytic cycle , intracellular multiplication of the.
Source: www.youtube.com
Check Details
Lytic cycle or virulent cycle; Definition lytic or virulent phages are phages which can only multiply on bacteria and kill the cell by lysis at the end of the life cycle. During infection a phage attaches to a bacterium and inserts its genetic material into the cell. It includes the following steps: Phages are present in every environment and shape.
Source: www.slideshare.net
Check Details
M13 uses the f pilus of e. Lytic or virulent phages are phages, which multiply in bacteria and kill the cell by lysis at the end of the life cycle. In the lytic cycle, a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus. There are 2 types of lifecycles that occur in the bacteriophage: Lysogenic cycle or.
Source: microbiologynotes.org
Check Details
Lytic cycle (virulent cycle) in this cycle, a bacteriophage enters bacteria and kills them. What are the steps in the life cycle of a bacteriophage? The family name comes from the ancient greek word ‘μικρός’ (mikrós), which translate to small, reflecting the size of their genomes. Their influence reaches far beyond the microorganisms they parasitize. Bacteria eating virus is called.